前言
openocd是一款开源的调试工具,当使用非mdk作为开发环境的时候会用到它。
如果你有一块热门的板子可以通过以下配置启动openocd:
openocd -f board/stm32f4discovery.cfg
如果你是特定的调试器interface和特定的目标芯片target:
或
这部分支持的interface和target可以从/tcl/interface和/tcl/target目录下获取。
以常见的jlink调试stm32f103为例,下面就是对应的两个cfg文件:
stm32f10x.cfg
jlink.cfg
# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0-or-later
#
# SEGGER J-Link
#
# http://www.segger.com/jlink.html
#
adapter driver jlink
# The serial number can be used to select a specific device in case more than
# one is connected to the host.
#
# Example: Select J-Link with serial number 123456789
#
# adapter serial 123456789
我在之前使用体验中,很快就用官方给的例子,成功调试起了STM32的单片机,毕竟东西能跑,也不曾细究原因。
可是心里的疑惑无法解答。
例如jlink.cfg里面这一行代码:
adapter是啥? 这个dirver又是啥?为啥可以这样子写?
心里会疑惑,如果我有一个完全新的芯片,市面上从来没有出现的芯片那么应该如何写呢?
本文的目的就是个解释上面这个问题,预计目标是看完这篇文章的小伙伴,可以为自己的芯片写对应的openocd配置。
正好我有手头上申请了几片国产的领芯微的MCU(LCM32F039),这款芯片原厂给的开发方式只适配了MDK。
它的寄存器也不是照抄STM32的,所以无法直接用ST的下载算法,那么我们以这颗芯片为例子,一起看看openocd到底是如何工作的。
介绍tcl
其实openocd采用了一个叫tcl的脚本语法,之前的那些cfg配置都是tcl语法的文件,去解析tcl从而实现了下载不同的芯片,选取不同的接口。
例如下面这行脚本实现的一个烧录功能,都是要到tcl的解释器里面去解析执行的。
那么我们很自然的就产生了一个疑问,如果这个芯片是从世界上刚刚诞生,从来没出现过。我应该怎么加下载算法呢?
这部分疑惑,我是在阅读了openocd的源码之后,才得以解除的。
它的源码和tcl脚本解释器是一一对应的,阅读源码,就可以了解到cfg文件应该怎么写了。
也就是说,你要加下载算法,就需要自己添加C文件,并且重新编译openocd。
所以我们先来看看如何编译openocd,至于到底tcl和C文件是如何对应的,我放到后面再讲。(我推荐大家能看懂源码的直接看源码,我写的罗里吧嗦的还会有疏漏,如果觉得看源码找不到头绪,再来看我的文字,我相信看过源码之后,对cfg文件应该怎么写,就不会再像之前那样子云里雾里了。)
编译原始的openocd
笔者要在windows下使用openocd,所以采取了MSYS2的方式。(Ubuntu下可以直接按照文档操作编译,但是Windows下的坑略多)
Note
MSYS2安装的时候会卡在50%处,此时断网等待约1分钟即可
在vscode的终端中配置msys2,msys2有四个环境可以选择,我们这里选择mingw64。
安装依赖&克隆仓库
先更新源再去安装依赖
编译jimtcl
成功后 可以用pkg-config命令找到jimtcl
编译openocd
安装对应的USB支持
编译
问题1:jimtcl is required but not found via pkg-config and system includes
我们把local环境临时添加进去即可
输入下面这行命令,可以找到jimtcl就行
总结
至此为止我们成功在windows上编译了openocd。
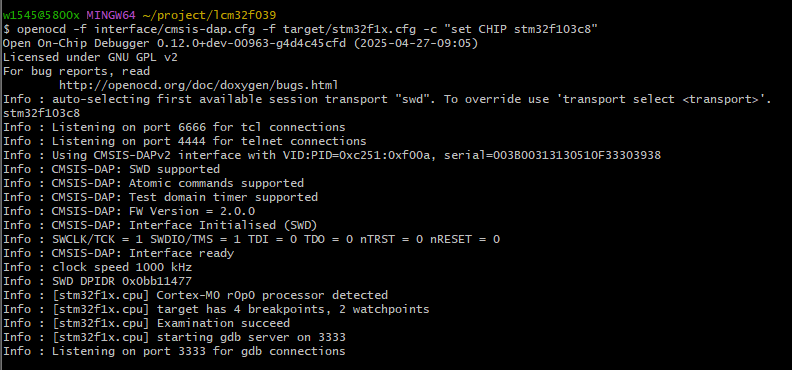
刚编译出来的openocd